What is spaced repetition
Spaced repetition is an evidence-based learning technique that involves reviewing information at increasing intervals over time. This method helps to combat the natural forgetting curve by re-exposing you to material just before you're likely to forget it, thereby strengthening memory retention for the long term.
Forgetting curve
The forgetting curve hypothesizes the decline of memory retention in time. This curve shows how information is lost over time when there is no attempt to retain it. A related concept is the strength of memory that refers to the durability that memory traces in the brain. The stronger the memory, the longer period of time that a person is able to recall it.
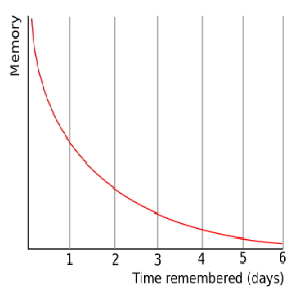
A typical graph of the forgetting curve purports to show that humans tend to halve their memory of newly learned knowledge in a matter of days.
Sign-in using Gmail ID
Spaced repetition
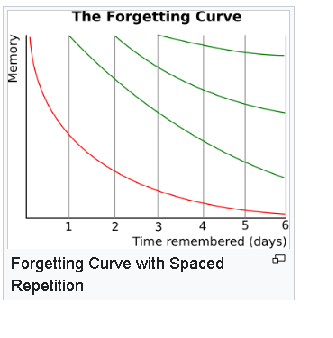
Spaced repetition is an evidence-based learning technique that is
usually performed with flashcards. Newly introduced and more difficult
flashcards are shown more frequently, while older and less difficult
flashcards are shown less frequently in order to exploit the psychological
spacing effect.
The use of spaced repetition has been proven to increase
the rate of learning.
Active recall
Recall in memory refers to the mental process of retrieving information from the past. Along with encoding and storage, it is one of the three core processes of memory. There are three main types of recall: free recall, cued recall and serial recall. Psychologists test these forms of recall as a way to study the memory processes of humans and animals.
Two main theories of the process of recall are the two-stage theory and the theory of encoding specificity.
Longterm memory

Long-term memory (LTM) is the stage of the Atkinson–Shiffrin memory model in which informative knowledge is held indefinitely. It is defined in contrast to sensory memory, the initial stage, and short-term or working memory, the second stage, which persists for about 18 to 30 seconds.
LTM is grouped into two categories known as explicit memory (declarative memory) and implicit memory (non-declarative memory). Explicit memory is broken down into episodic and semantic memory, while implicit memory includes procedural memory and emotional conditioning.
Use QuizGlobe to get the edge in the competitve exams.